
NLP, or Neuro-Linguistic Programming, is a complex and often misunderstood field that endeavors to decode the intricacies of human behavior. Pioneered in the 1970s by Richard Bandler and John Grinder, NLP seeks to bridge the gap between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors by harnessing the power of language, neurology, and programming. "NLP is a labyrinthine quest, an unquenchable curiosity about humankind, leaving behind a labyrinth of techniques," says Richard Bandler, the co-creator of NLP.
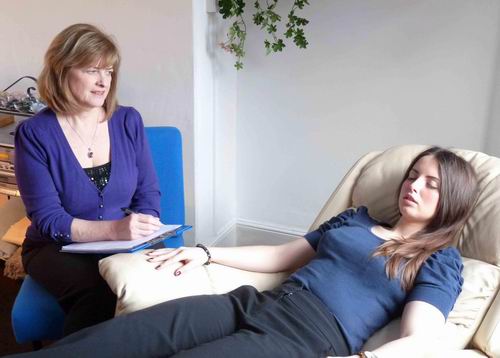
Timeline Therapy is a therapeutic approach aimed at assisting individuals to acknowledge and free themselves from negative emotions and restrictive convictions that obstruct their aspirations and joyous existence. It was created by Dr. Tad James in the 80s and is built on the NLP foundations. Timeline Therapy's purpose is to help people conquer past traumas and negative occurrences, release negative feelings and beliefs that hold them back, and retrain their mind to think positively and constructively. This leads to progress in life, accomplishment of goals, and an enriched existence.

What exactly is visual-spatial intelligence? Simply put, it's the capacity to understand, analyze, and transform visual information in the environment. The brain is able to think with images, detect spatial relationships among objects, and manipulate them mentally. This cognitive ability has tremendous impact in our daily lives, whether it's finding our way through an unknown city or solving puzzles and playing video games. Visual-spatial intelligence is also of immense significance in fields such as engineering, art, design, and architecture. In this write-up, we delve into what visual-spatial intelligence entails, its significance in daily life, and tactics for fostering and boosting this cognitive ability.

Defining Kinesthetic Intelligence: It refers to the ability to use one's body effectively and efficiently to complete tasks and solve problems. Individuals with high kinesthetic intelligence tend to have good physical coordination, balance, dexterity, and control over their movements. They excel in activities requiring physical movement and manipulation, such as sports, dance, and theater.

The Silva Method, popularly known as Silva Mind Control, is a journey of self-discovery and improvement. Conceived in the 1960s by José Silva, this self-help program is predicated on the notion that humans possess the power to draw from their intrinsic resources to better their lives. By incorporating visualization and meditation practices, the Silva Method endeavors to assuage stress, sharpen focus and help people attain their aspirations.

Alexithymia is a condition characterized by difficulty identifying, expressing and understanding emotions. People with alexithymia often have difficulty describing how they feel, and may struggle to differentiate between emotions and physical sensations. They also tend to have limited imagination and daydreaming, and may have difficulty understanding and responding to the emotions of others. Despite its prevalence, alexithymia is often overlooked and misunderstood. Recent research has shed light on the causes, symptoms and impact of this condition on mental health and relationships.

Loneliness, a pervasive and debilitating feeling of isolation, can afflict anyone, indifferent to demographics such as age, gender, and background. It is a state of disconnection that exacts a heavy toll on an individual's mental and physical health. However, it is possible to transcend the debilitating sensations of loneliness and attain a sense of connection. By harnessing self-awareness and forming relationships, one can fortify their resilience and move beyond loneliness towards a sense of community. In this exposition, we delve into the root causes and repercussions of loneliness, the significance of self-awareness and relationships in fostering resilience, and practical approaches to transitioning from loneliness to belonging.

Personality assessments are utilized to measure an individual's defining traits and behaviors. These evaluations provide an insight into how a person interacts, thinks, and reacts in varying scenarios. They've been in use for years across various domains such as therapy, education, and the workplace. Personality testing originated in the early 20th century with the creation of the Woodworth Personal Data Sheet, which was implemented during WWI to screen soldiers for psychological afflictions. Ever since, multiple personality assessments have emerged, each with their own distinct methodology for evaluating personality.
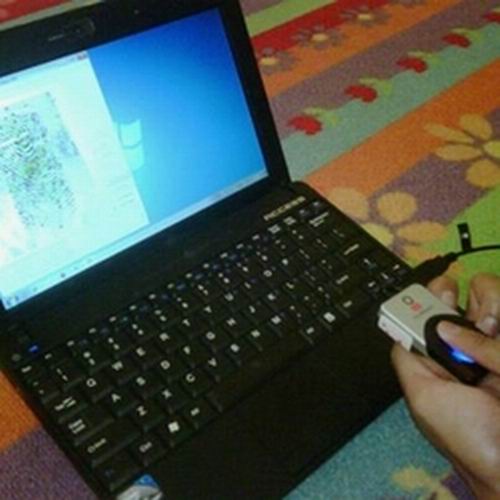

In the quest for self-discovery and optimal personal development, the Dermatoglyphics Multiple Intelligence Test (DMIT) has emerged as a groundbreaking tool. This non-invasive, scientific analysis of unique fingerprint patterns is believed to offer profound insights into an individual's innate talents, cognitive strengths, and personalized learning styles.

Musical intelligence refers to the capability to comprehend, produce, and appreciate music, including the ability to discern pitch, melody, harmony, rhythm, and timbre. With this aptitude, individuals can identify musical patterns, grasp various forms of music, and even create or improvise their own tunes. The enhancement of musical intelligence can commence from an early stage, and it can have a constructive impact on various elements of human progress, such as emotional, cognitive, and social growth. This article delves into the traits of musical intelligence, the ways to foster it, and its relationship with other forms of intelligence.
|










